How Global Connectivity Impacts the Convergence of Information Technology and Operational Technology

Previously, operational technology (OT) was isolated solely in the machines used for manufacturing, energy maintenance, and logistics. Though many of these tools for monitoring had digital controls, they were closed and not connected to a network.
The Modern Advancement of Operational Technology (OT)
Today, however, we are witnessing a convergence between information technology (IT) and the databases and protocols used to collect data, and OT, where the monitoring and controls of equipment can not only be done from a centralized location but can also be managed halfway around the world with the power of the Internet.
This dramatic advancement in machine-to-machine (M2M) connectivity and communication has led to data produced by these devices to be collected and analyzed in real time as a means to increase business productivity, enable preventative maintenance, and improve efficiency.
However, OT connected with Internet begins to face some of the same security challenges IT deals with on a daily basis. The difference is that vulnerabilities in an OT system can leave critical infrastructure at risk of sabotage that can result in the failure of a business if not addressed.
Major Trends and Challenges in the Advancement of OT
There are many prime examples of how OT and IT are converging within enterprises today:
- SCADA (Supervised Control and Data Acquisition) is a technology architecture that has combined network data communications used for IT enterprise management into the controllers and devices used within process plant machinery. A single operator is able to monitor and command devices from a single location without the need of being on the manufacturing or process floor itself.
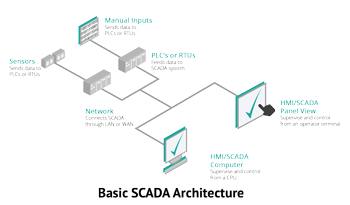
For SCADA systems to work effectively, especially on a global scale, there needs to be a strong networking infrastructure in place providing accurate and effective management of the system. -
The Internet of Things (IoT) is another example of OT convergence. This consists of a network made up of physical objects that communicate with other machines and collect data for efficiency and productivity. Today, IoT is everywhere! It ranges from consumer devices such as smoke alarms to smartwatches, and large enterprises devices in the form of health monitors for the medical industry or traffic flow sensors for manufacturing.
- Sensor data is an integral component of the increasing reality of the IoT environment with almost any business asset capable of being outfitted with a unique identifier (UID) and the capacity to transfer data over a network. However, much of the data produced and transmitted through these sensors is huge. Therefore, collecting the results could be time-consuming depending on the transport.
Global enterprises need to collect this information in real time to develop big data analytics with the potential to deliver significant impact on operational strategy and business value.
Thus, the emergence of Operational Technology into IT infrastructure requires some key major elements:
- A secure, global network with enterprise-grade quality that provides fast and reliable, connectivity worldwide
- Simple and quick deployment of the global infrastructure with on-demand scalability
- End-to-end network visibility from data collection points to the process systems around the globe
And That’s Exactly What Aryaka Provides
Aryaka is uniquely positioned to help companies converge Operational Technology and Information Technology. By allowing seamless, high quality, secure, and accelerated connectivity across the globe. Aryaka creates unparalleled possibilities to remotely monitor and control assets, equipment, and processes in real time. Our unique approach to global connectivity combines secure connections that provide superior performance compared to MPLS or the public Internet.
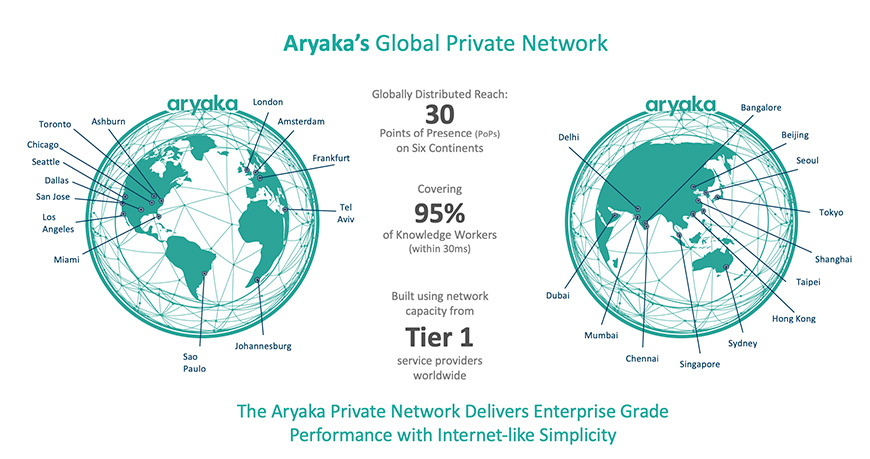
Aryaka’s global private network provides Layer 2 full-mesh connectivity built with 30 points of presence (PoPs) around the world. The network is able to bypass the public Internet and eliminate congestion and packet loss, through a secure global transport. It also provides end-to-end visibility on how your data is being transported across the globe from collection points to the processing locations.
We invite you to connect now and give us a try.
And to learn more, download our latest white paper, CIO Solutions for Big Data and Manufacturing.




